Guerra Scale Of Interactivity
Written & Researched by: Ivan Teh RunningMan
The Guerra Scale Of Interactivity was developed by Tim Guerra and Dan Dan Heffernan in March 2004. It outlines the range of electronic content, and user experience, in relation to online learning.
When the Guerra Scale Of Interactivity is applied to the development of electronic learning (e-learning) software, or online learning, it makes reference to 2 computer science concepts: Interactivity and Engagement.
 |
Interactivity refers to how much, or how little, the computer program / software accepts and responds to input from people.
Engagement refers to quality of user experience with the electronic content, in particular, factors that cause the user to want to use it longer or more frequently.
.....
The defining characteristics of the Guerra Scale Of Interactivity are as follows:
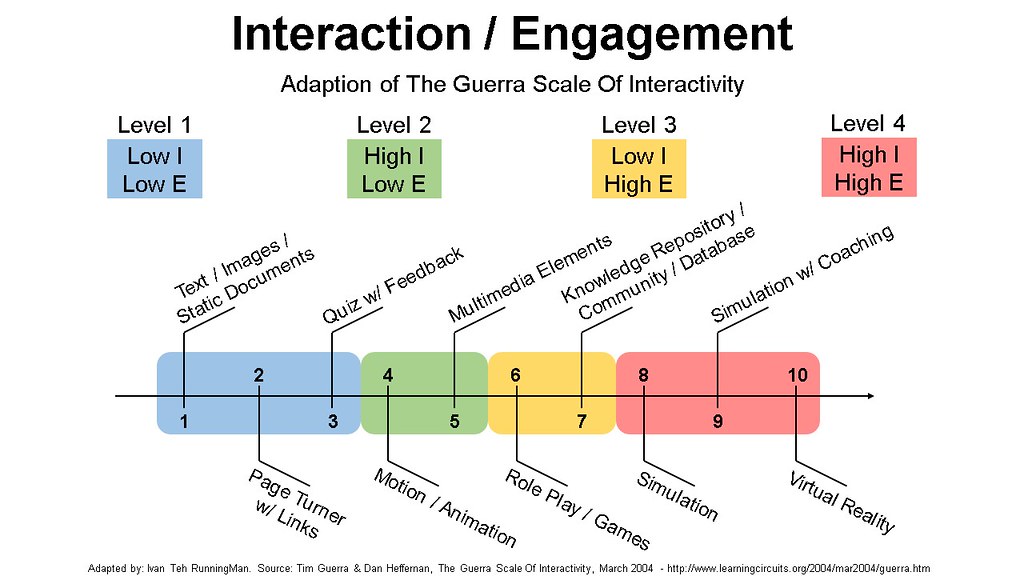
GS1 is a simple, static text, image, or document, where interactivity is limited to scrolling
GS2 includes the use of hyperlinks within the text, image, or document, allowing users to immediately jump to the relevant section
GS3 incorporates a dynamic feedback, quiz, or test, either at the end, or midway throughout
GS4 introduces simple movement to the text and images
GS5 adds audio or video elements, or more complex, elaborate moving graphics / animation
GS6 allows for user input, through e-activities that have a relevant context
GS7 refers to a database or electronic library that users may reference, but also includes community forums, and online group discussions
GS8 uses real world processes in realistic e-scenarios with a relevant context, which may have branching methodology which is dependent on user input
GS9 has the inclusion of real time advice / instructions from a top performer, industry professional, line manager, trainer, or mentor
GS10 features a full immersive environment in which the user has near total control, with boundaries defined by real world processes and a relevant context, best used for abstract concepts
.....
The Guerra Scale Of Interactivity is often applied to the development of e-learning software to measure student engagement.
Each step up "represents an increase in complexity, functionality, development time, demands for programming skill, demands for instructions design versatility, and demands for more patience and attention from subject matter experts".
It is a good tool to reference when selecting the appropriate technology for e-learning development, as a higher interactivity or engagement score means learners are more likely to use, or revisit, the content.
However, it does not measure the actual amount learnt by the student, assuming a greater amount of knowledge is retained due to higher interactivity or engagement.
It also does not indicate that any 1 method is "better", or "more preferable", as compared to another method. It makes no sense to teach all educational content using solely 1 method on the Guerra Scale Of Interactivity.
Furthermore, the Guerra Scale Of Interactivity does not properly account for technologies developed after 2004, which includes social networking, augmented reality, and other Web 2.0 tools.
In conclusion, the best online learning experiences typically involve a mix of content delivery. By utilising a variety of e-learning methods, and keeping the Guerra Scale Of Interactivity in mind, content developers can deliver more engaging training while retaining cost effectiveness.
.....
Source Attributions:
Tim Guerra & Dan Heffernan, "The Guerra Scale Of Interactivity" in The Guerra Scale: Learning Circuits, published March 2004. Retrieved from http://www.learningcircuits.org/2004/mar2004/guerra.htm
Jefferson Flanders, "The Guerra Scale: Reflections" in MindEdge Learning Workshop, published December 2009. Retrieved from http://learningworkshop.mindedge.com/2009/12/05/the-guerra-scale-reflections/
Lim Kin Chew, "Quality Matters in E-Learning" in eUniSIM Blog, published August 2010. Retrieved from http://eunisim.blogspot.sg/2010/08/quality-matters-in-e-learning-4.html
Victor Fester, "Are all Apps Equal? Evaluating Apps to Maximise Student Engagement" in Shar-e-fest Symposium, published October 2012. Retrieved from http://api.ning.com/files/CCUb6jnzEC8VzxSHsm2vrs6n9j2J7i-NkfA4s1ciAYxx8Ymj6y6Bq4NqSMIx6CmQfmcu5TO7ZGIdvthPfpUUrc-wiNaSZ3g9/AreallAppsEqual.pdf
.....


CONVERSATION